
Many people might wonder why a standard container is relatively inexpensive, while an energy storage container is significantly more costly — often several times higher in price. What makes it so special? Let’s take a closer look at the key components and design features that set energy storage containers apart:
Main Materials
Standard containers typically use ordinary low-carbon steel with basic anti-corrosion treatment, sufficient for transportation needs. In contrast, energy storage containers are made from high-strength, corrosion-resistant steel, treated with advanced anti-corrosion processes. Their anti-corrosion standards are much stricter, and they must also meet insulation, fire resistance, explosion protection, and environmental standards.
Overall Structure
While standard containers are primarily designed for compressive strength and impact resistance with empty internal space to support cargo stacking, energy storage containers are engineered to accommodate battery racks and electrical equipment securely. Their structural frame must ensure balanced load-bearing to prevent displacement caused by vibration, with specific areas reserved for cable routing and ventilation ducts. This results in a significantly more complex design.
Sealing and Ventilation
Standard containers rely on basic sealing to protect against rain and feature simple ventilation holes for moisture control. Energy storage containers, however, require both airtight sealing (to prevent dust and water ingress) and controlled ventilation, often incorporating cooling air vents and explosion-proof ventilation systems.
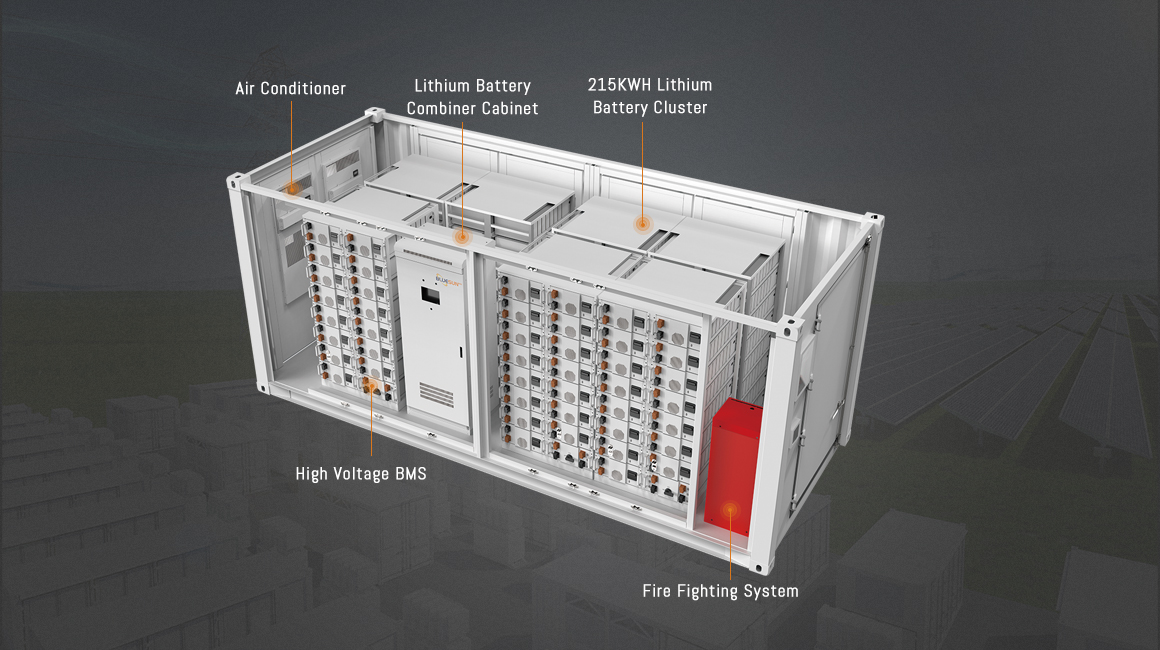
Depending on the system’s requirements, energy storage containers are equipped with customized fire protection systems, including smoke detectors, temperature sensors, and automatic fire suppression units. Common suppression agents such as heptafluoropropane enable rapid response in the early stages of a fire, ensuring the safety of both equipment and personnel.
To manage the heat generated by batteries and electrical components, air-cooled containers use integrated systems like air conditioners, fresh air inlets, and ventilation fans. These help dissipate heat effectively and maintain optimal operating temperatures for all equipment, thereby extending the service life of the entire energy storage system.
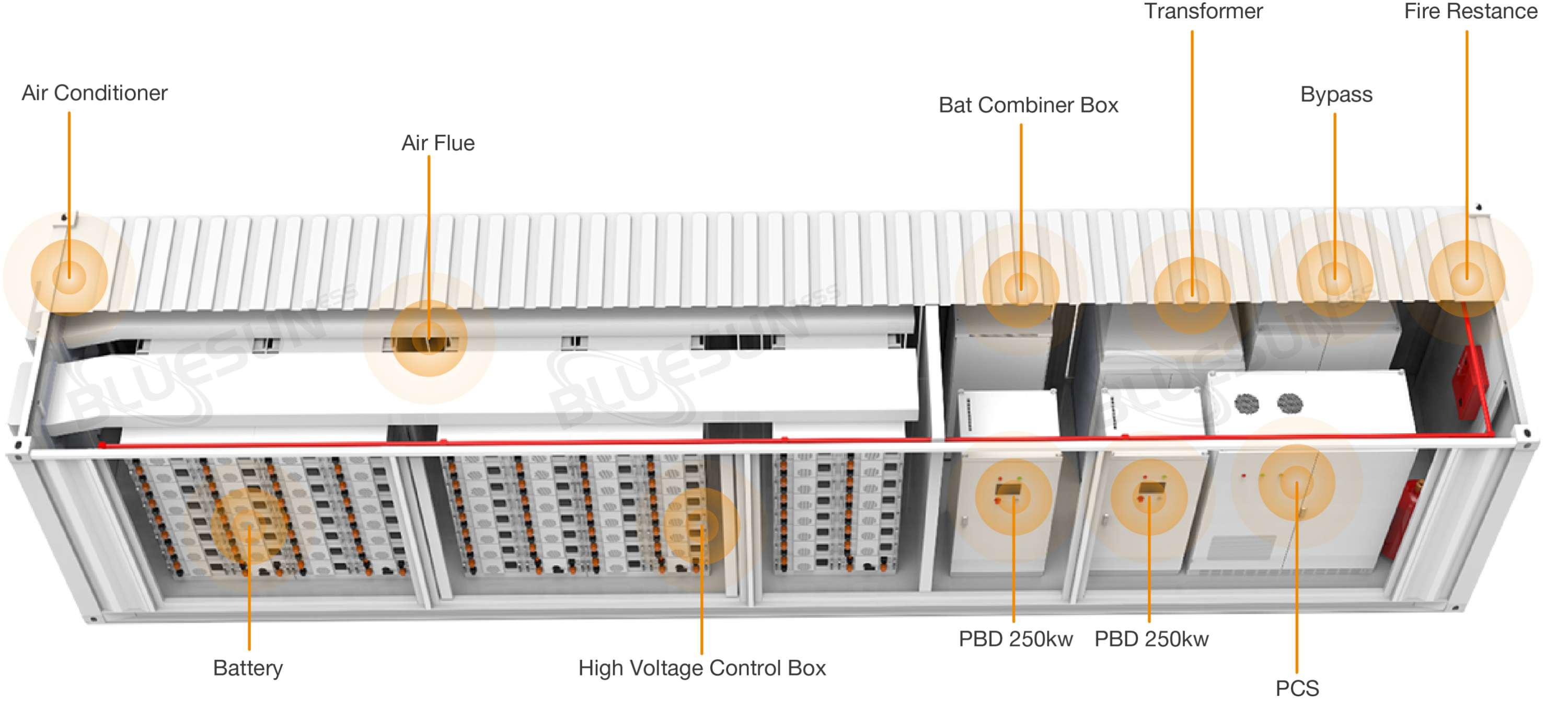
Energy storage containers integrate multiple electrical devices and components, requiring precise installation and reliable connections to ensure stable system performance. Each container undergoes strict quality control and comprehensive testing, including electrical and safety performance assessments, before deployment.
For marine export or road transportation, containers must comply with relevant shipping regulations. If transported as a complete system, they must also meet dangerous goods transportation standards, with certifications such as Classification Society certification and dangerous goods packaging certification.
In summary, the cost of an energy storage container goes far beyond the price of a simple metal box. From materials and structural design to integrated fire protection, temperature control systems, precision wiring, and required certifications, every aspect contributes to its high value. An energy storage container is not just a “battery container” — it is a critical infrastructure that ensures the safety, stability, and long-term efficiency of your energy storage project.
When investing in an energy storage container, focus on quality and design — not just the price — to safeguard your project and maximize long-term returns.